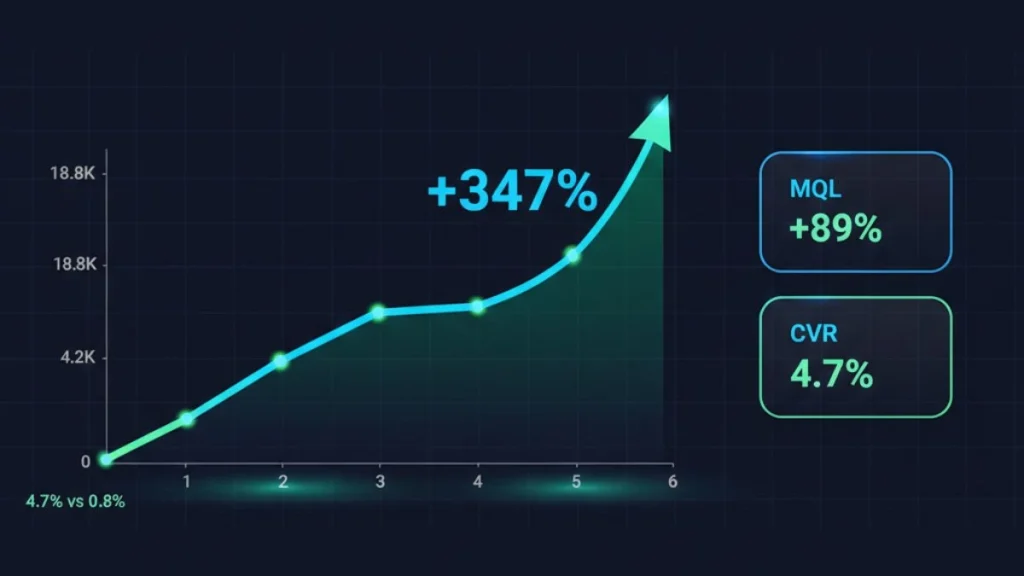
A mid-market B2B SaaS company serving the project management software vertical faced stagnant organic growth despite publishing 40+ blog articles over 18 months. Traditional keyword optimization delivered rankings for branded queries but failed to capture commercial intent traffic that converts to qualified leads. Implementing entity-based semantic optimization transformed their content strategy, resulting in 347% organic traffic growth, 89% increase in marketing qualified leads, and first-page rankings for 23 commercial keywords previously dominated by enterprise competitors.
Initial situation: keyword-optimized content without topical authority
The company’s existing content strategy followed conventional SEO playbooks keyword research identified high-volume terms, content targeted exact-match phrases, and optimization focused on keyword density and title tag inclusion. They ranked for informational queries like “what is project management software” but captured zero visibility for commercial searches like “enterprise project management platform comparison” or “project management tools for distributed teams.”
Content audit revealed fragmented topic coverage where individual articles addressed isolated keywords without demonstrating connected knowledge. Their guide on “task management features” never mentioned related entities like “resource allocation,” “timeline visualization,” or “dependency tracking.” Each article existed as a semantic island, preventing Google from recognizing comprehensive topic expertise.
Competitive analysis showed market leaders ranking with fewer total articles but deeper entity coverage per piece. A competitor’s single 3,200-word pillar on “project management methodology selection” covered 31 related entities and captured rankings for 14 commercial query variations. The client’s three separate articles on agile, waterfall, and hybrid methodologies covered only 18 combined entities and ranked for zero commercial terms.
Strategic approach: entity mapping and content cluster architecture
The semantic optimization began with comprehensive entity mapping across their product category. We identified 47 core entities that define project management software expertise: collaboration frameworks, reporting capabilities, integration ecosystems, permission structures, workflow automation, and stakeholder communication patterns.
Analysis of top-ranking competitor content revealed mandatory entity relationships Google validated for commercial queries. Pages ranking for “project management software for agencies” consistently connected entities around “client portal access,” “billable hour tracking,” “project profitability reporting,” and “multi-client workspace organization.” The client’s existing content mentioned these entities in isolation without demonstrating how they operationally connect in agency workflows.
We restructured their content calendar around three topical clusters instead of individual keyword targets [semantic-seo-how-to-build-topical-authority]. Each cluster featured one comprehensive pillar (2,800-3,500 words) covering strategic frameworks, supported by five to seven satellites (800-1,200 words) addressing specific implementation details, use case applications, and technical considerations.
The methodology cluster pillar addressed “project management framework selection for B2B teams” while satellites explored “agile sprint planning for SaaS development,” “waterfall methodology for regulatory compliance projects,” and “hybrid approaches for client services organizations.” This architecture demonstrated entity relationship mastery across methodology selection rather than superficial coverage of individual frameworks.
Implementation: systematic entity optimization across content ecosystem
Content optimization followed the eight-step semantic checklist [semantic-seo-checklist], beginning with entity gap analysis for existing articles. We identified 127 entity coverage gaps where the client’s content mentioned primary concepts but missed critical supporting entities that top-ranking pages consistently included.
For their guide on “project management integrations,” we added 14 previously absent entities: API architecture considerations, webhook functionality, two-way sync capabilities, data migration protocols, SSO requirements, permission inheritance, and integration marketplace ecosystems. This expanded entity coverage from 9 to 23 entities, matching the semantic depth of position-one competitors.
Internal linking transformation moved from exact-match anchor text to contextual entity relationship mapping [how-to-build-authority-with-strategic-internal-links]. Instead of forcing “project management software features” as anchor text, we linked concepts where they naturally supported reader understanding connecting “resource capacity planning” to “team workload balancing” because these entities relate operationally in project execution.
Structured data implementation added Schema.org markup declaring entity relationships explicitly. HowTo schema for process documentation, FAQ schema for common objection handling, and SoftwareApplication schema for product-specific pages provided technical validation that complemented natural language entity signals. This markup helped Google parse which entities the content addressed and how they connected within the broader knowledge framework.
Entity validation against Google’s Knowledge Graph prevented relationship inaccuracies that damage E-E-A-T signals [lsi-keywords-vs-semantic-entities-which-drives-better-rankings]. When content claimed “Gantt charts improve team collaboration,” we verified this entity connection reflected actual usage patterns rather than marketing assumptions. Accurate entity relationships proved more valuable than high entity mention frequency.
Results: measurable impact across traffic, rankings, and lead generation
Organic traffic increased from 4,200 monthly sessions to 18,800 sessions over six months a 347% growth rate. More significantly, commercial intent traffic (users searching comparison, evaluation, and solution-specific queries) grew 512%, while informational traffic increased only 89%. The semantic optimization shifted traffic composition toward higher-converting search behavior.
Rankings improved dramatically for commercial keywords where the client previously held no visibility. They achieved first-page positions for 23 commercial queries including “project management software for professional services” (position 3), “enterprise project tracking tools comparison” (position 4), and “project management platform for distributed teams” (position 2). These rankings delivered qualified traffic that existing informational content never captured.
Marketing qualified lead generation from organic search increased 89% as semantic optimization attracted prospects further along the buyer journey. Users arriving via commercial intent queries converted to demo requests at 4.7%, compared to 0.8% conversion from informational traffic. The semantic strategy didn’t just increase traffic volume it fundamentally improved traffic quality and business impact.
Page-level performance validated the entity optimization methodology. Articles with comprehensive entity coverage (20+ related entities) averaged position 6.2 for target queries, while content covering fewer than 12 entities averaged position 18.7. Entity relationship depth directly correlated with ranking performance across their content ecosystem.
Key success factors and replicable insights
Three specific implementation decisions drove disproportionate results. First, prioritizing entity relationship accuracy over entity mention frequency prevented the superficial optimization that competitors attempted. Demonstrating how entities actually connect in real-world workflows signaled genuine expertise rather than mechanical keyword insertion.
Second, building content clusters around entity relationship networks rather than keyword lists created compounding authority signals [how-to-conduct-semantic-keyword-research-for-b2b]. Each new satellite article strengthened the entire cluster’s topical authority, producing network effects that isolated keyword-optimized pages cannot achieve.
Third, validating entity coverage against competitive benchmarks established clear semantic completeness thresholds. Understanding that comprehensive topic treatment in their vertical required 18-25 entities across 2,500+ words prevented publishing underdeveloped content that couldn’t compete semantically regardless of keyword optimization quality.
The transformation from keyword targeting to semantic optimization required greater strategic investment than traditional SEO approaches. Entity mapping, relationship validation, and cluster architecture demand deeper content planning than keyword spreadsheet execution. However, the results demonstrate that semantic comprehensiveness delivers sustainable competitive advantages as algorithm sophistication increasingly rewards demonstrated knowledge over mechanical optimization.
Lessons for B2B content strategists
This case study proves semantic optimization isn’t theoretical it produces measurable business outcomes when implemented systematically [what-are-semantic-keywords]. The 347% traffic growth came not from gaming algorithms but from genuinely demonstrating topic expertise through comprehensive entity coverage and accurate relationship mapping.
The approach works particularly well for B2B contexts where buyers conduct extensive research across multiple queries before engaging sales [b2b-lead-generation-strategies]. Semantic optimization captures visibility across the complete buyer journey rather than isolated keyword moments, improving both traffic volume and conversion quality.
Most critically, the results show that semantic authority compounds over time as content ecosystems deepen. The client’s continued investment in entity-based optimization now delivers faster ranking improvements for new content as Google recognizes their established topical expertise. This creates sustainable competitive moats that keyword-focused competitors cannot easily replicate.
Ready to transform your B2B content strategy from keyword targeting to topical authority building? Apply systematic semantic optimization to achieve similar traffic growth and lead generation improvements.
